SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, and is the industry standard when it comes to safe and secure online transactions between websites and users.
Put simply, the SSL technology allows for an encrypted connection to take place between a user's web browser and the web server of the website that the customer is browsing.
SSL ensures that any data or information a user submits to the website, such as credit card information to make a purchase, will be protected and private.
There are a few steps that a website owner (e-commerce store or not) must take to obtain an SSL certificate for display on the e-commerce store, including verifying the identity of the website and the company behind the store.
Users of your e-commerce store can quickly and easily tell if you are secure by checking for a small lock icon in the browser address bar. Clicking on that lock icon will give more information about the certificate used by each website.

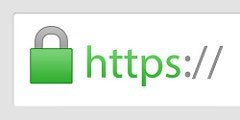
Here's an example of how the Shopify website shows up as being secure. The exact look may differ depending on what web browser you use, but the general concept remains.
Note the small lock icon and green color, and the 's' in 'https' that are both indicating that a security (SSL) certificate is used.
To view more information about the SSL certificate, a user can click on the Details link in the image above, then click View Certificate.
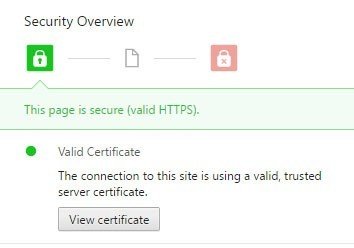
A new certificate details window will open and users can view information such as issued and expiration dates of the certificate, as well as what the certificate does (what's the purpose).
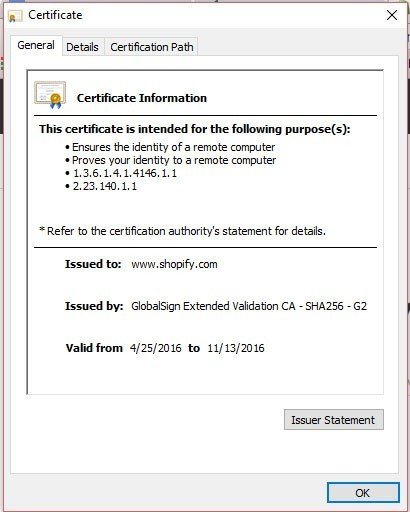
Web sites, not limited to e-commerce stores, that use SSL certificates can increase the safety and security for their customers to enter financial and personal information into without needing to worry about their personal information being compromised.
What is PCI DSS Compliance
PCI DSS stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard.
This standard was created in an attempt to help protect credit card companies by requiring that merchants and companies that process, store or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment.
It's administered and managed by the PCI SSC ("Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council"), a global forum created in 2006 by the 5 major credit card companies (Discover, JCB International, Visa Inc., American Express and MasterCard) in an attempt to enhance and implement security standards to protect credit card account data.

While federal law in the United States doesn't require compliance with PCI DSS, a number of state laws do require this, as well as a number of credit card companies, including Visa and MasterCard.
Basically, if you are a merchant (have a merchant ID) who processes, stores or transmits credit or debit card information, even once, you'll most likely be required by one of the credit card companies, at a minimum, to comply with the PCI DSS.
Complying with PCI DSS
Being compliant with PCI DSS means meeting the following a list of 12 requirements:
- Use a secure network where a firewall configuration is installed and maintained in order to protect credit card data.
- Personalize and change system passwords instead of using vendor-supplied default passwords.
- Always make sure any stored cardholder data you have is protected and secure.
- Whenever you transmit cardholder data across public networks, make sure the transmission is encrypted.
- Use anti-virus software on your network and keep it up to date.
- Make sure that any systems or apps that you develop are secure.
- Keep cardholder data very private within your business. Not everyone should have access to the data.
- Make sure that anyone who logs into a computer on your secure network has a unique identifying number or username.
- Make sure that physical access to cardholder data is restricted.
- Implement tracking and monitoring of all access to the stored cardholder data and your network resources.
- Conduct frequent tests to make sure your security implementations are working.
- Have an "Information Security" policy that is made available to people who are given access to your networks, such as contractors or your employees.
While it may seem like a daunting task to keep up with these requirements, e-commerce stores that use some third party e-commerce platforms, such as Shopify, Bigcommerce and others, will have all of these requirements taken care of by the third party and won't have to maintain a separate compliant network.
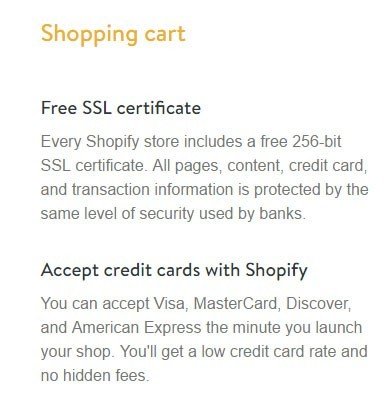
For example, signing-up for Shopify means your ecommerce store will get an SSL certificate and the assurance that "all pages, content, credit card, and transaction information is protected by the same level of security used by banks."
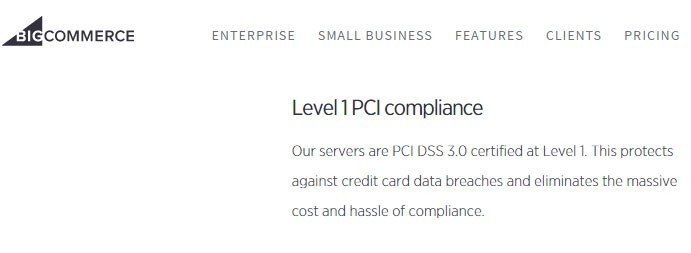
Bigcommerce provides PCI compliance as well when you host your ecommerce store with them:
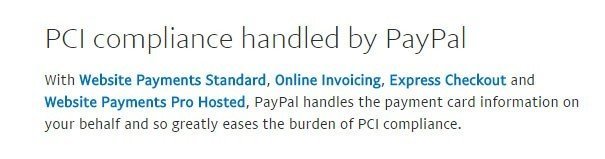
PayPal can also, in most cases, handle PCI compliance:
However, if you want to process payments yourself and collect and/or store any bank card data directly on your network, you'll need to make sure your business is compliant with the PCI DSS requirements.
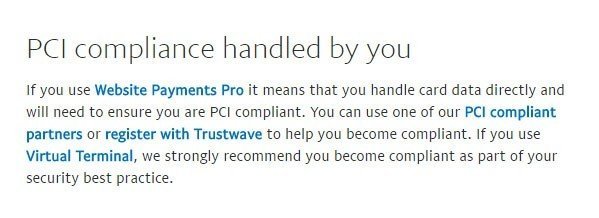
Even some features of PayPal still require you to handle your PCI compliance yourself, such as Website Payments Pro. This is because even when you use this feature, you'll still be handling card data directly in your store.
A third party app that makes accepting payments easier or more streamlined for convenience, but that still requires you to store and process the payment information yourself will require that you handle compliance yourself, while a third party app that does the payment processing and storing for you, will usually include compliant features so you won't have to worry about it yourself.
Keep users informed with a Privacy Policy
Customers of your e-commerce can be very concerned about the security of their personal data, and understandably so.
And, to make sure your customers feel comfortable shopping on your store, you should make mention of the security of user data in your Privacy Policy agreement, and note that your store uses SSL certificates.
You can let these customers know that their data will be secure, whether you have implemented the PCI compliance requirements yourself, or your store is secured by using a third party for your payment data collection, processing and storing (Shopify, Bigcommerce etc.)
Here are a few examples of how some e-commerce websites have kept their customers informed and their data secure.
Nike
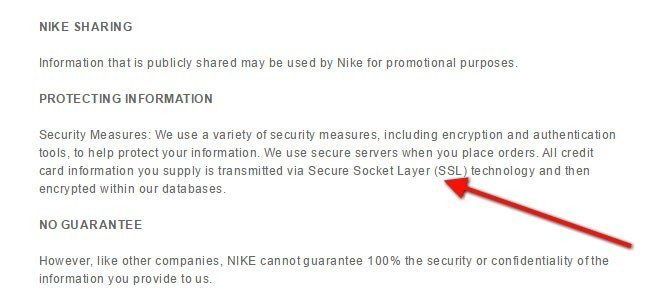
Nike includes a section titled "Protecting Information" its Privacy Policy.
Within this section, Nike lets customers know that a variety of security measures are used including encryption, authentication tools, and SSL technology for all credit card information Nike collects from customers.
Native Union
When you're shopping or browsing on Native Union's website, SSL certificate isn't activated until you place something in your shopping cart and take steps to purchase it by entering your payment information:
![]()
After you place something in your cart, the https is activated, and the green lock is visible:
![]()
Notice the secure payment icon that also lets users know that there is security in place:
![]()
Enjuku Racing
Enjuku Racing includes a section on "Security" in its Privacy Policy.
This section in their agreement lets users know that if a user provides Enjuku Racing with credit card information, "the information is encrypted using secure socket layer technology (SSL) and stored with AES-256 encryption."

Is SSL required or not
If you want to process payments yourself and collect and/or store any bank card data directly on your network, you'll need to make sure your business is compliant with the PCI DSS requirements, thus requiring SSL certificates.
If you use a third party service to process payments, you may still need an SSL, but most third parties like Shopify or Bigcommerce will take care of security for you, so you won't need to worry about the certificates.
However, other platforms like PayPal's Website Payments Pro will allow you to collect some bank card data yourself, but this requires you to make sure your e-commerce store is PCI DSS compliant.
While there isn't currently a law that requires you to have a "Security" clause in your Privacy Policy that will inform your customers about your store's use of SSL certificates and how their credit card data is protected by your store, privacy laws in general demand that you take care of your customers' personal data by protecting their privacy and keeping them informed of your practices, including your policies on safety and security of data.
This is why it's required to have a Privacy Policy for your e-commerce store where you can disclose your policies and practices.
Having an SSL certificate can significantly boost the safety and security of the user data you collect from your customers. Including information about your security practices in your Privacy Policy can also help these customers feel safe by letting them know how their data is actually protected.

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.