Do you send out email newsletters? If you do, you're collecting personal data in the form of email addresses.
If you have any subscribers who reside in the EU, you need to be aware of how the GDPR affects your newsletters.
Email marketers now have two choices. Comply with the new European Commission's law - the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) - or block access to your site for the 508 million people in the EU - the world's third largest population.
Thankfully, email marketers and anyone else with a newsletter only need to make a few simple changes to make their newsletters compliant with the law.
Keep reading, and we'll break down compliance and email marketing in the our new GDPR world.
- 1. Do You Need to Comply with the GDPR?
- 1.1. An Email Marketing Example
- 1.2. What Consent Requires
- 2. The New Consent: Your GDPR Newsletter Checklist
- 3. Single Opt-In vs Double Opt-In
- 3.1. Single Opt-In
- 3.1.1. Pros of Single Opt-In
- 3.1.2. Cons of Single Opt-In
- 3.2. The Double Opt-In
- 3.2.1. Pros of Double Opt-In
- 3.2.2. Cons of Double Opt-in
- 4. Make Unsubscribing Easy
- 5. Conclusion
Do You Need to Comply with the GDPR?

If you collect email addresses, then you collect personal data. If you collect personal data from residents of the EU, the GDPR applies to you.
It's simple. If you comply, you're free to continue operating as normal. However, fail to update your data standards and you could see a fine of up to 4% of your gross annual turnover - not profit.
The fines are capped at 20 million Euro, which is a hefty sum even for the big fish.
The European Commission spent the last several years worrying about personal data and the way it was used, and it's hard to blame them for that.
Companies went rogue with private, personal details provided in good faith (and taken without consent). Other organizations gathered virtual mountains of data without making their data gathering practices clear. Even more companies did all this with lax security practices that made personally identifiable data vulnerable to theft.
Europe's government looked at the infringement on privacy for profit and said: "No more."
Now, if you want to collect the personal data of a European resident or citizen - or anyone with an EU IP address - you may have to ask and get consent.
Consent now involves both choice and control. The person who owns the data is in charge - not your data controller. If the individual must hand over their data to use your site, then their consent isn't freely given.
It might sound strange, but it's also good business. When individuals control their data, you're delivered an opportunity to burnish your reputation and build trust with your customers.
An Email Marketing Example
You send out a newsletter that's highly-tailored to your target audience. Sometimes, your newsletter receives sponsorship from brand partners. A new partner asks you to hand over your email list as part of your agreement.
Under the new GDPR definition of consent, you cannot do that unless you update your Privacy Policy to disclose this, and specifically request consent from your subscribers to share the information.
Why?
Because sharing their data isn't necessary for them to get a newsletter that you're sending out.
You can ask customers to consent to your handing out their data, but they must have two clear choices and their choice to opt-out must not impact their current subscription.
If you want the option to sell your email list in the future, you need to add that condition to your newsletter Privacy Policy. You can't bundle the options. Users must be able to sign up for your newsletter and opt-out of the sharing of their data at the same time.
What Consent Requires

Explicit consent requires several things:
- A positive opt-in
- Clear and specific statements of consent
- Granular consent - separate for different things: cookies, Privacy Policy, etc.
- Separate consent requests from other Terms and Conditions
- Refreshed consent upon changes to Terms
- Avoiding consent as a precondition to service
- Opportunities to withdraw consent
The New Consent: Your GDPR Newsletter Checklist

It's more than you may be used to, but obtaining GDPR-compliant consent isn't so hard.
Ask yourself these questions about your current consent or opt-in practices to see if you need to change your newsletter sign-up mechanism:
- Do you have a lawful basis for processing data? (If you're sending a newsletter, then the answer should be yes.)
- Have you made the consent request for your newsletter separate from other things like your privacy policy, cookies, or terms and conditions?
- Did you ask new subscribers to positively opt in?
- Is your opt-in written in easy language that most people could easily understand?
- Are you specific about what emails you'll send? If you're sending more than a newsletter, do you have an option to opt-in or out of other emails?
- Will any third parties have access to the data? Have you shared that in your consent form?
- Is it easy for individuals to withdraw their consent?
- Will withdrawing consent have no impact on the user's relationship with your service?
- Do you have age-verification measures, if applicable?
If you answer 'yes' to all nine of these questions, then you're ready to send GDPR-compliant newsletters and recruit new sign ups.
Any 'no' answers mean you still have some work to do.
Single Opt-In vs Double Opt-In

When setting up your newsletter, you have two options for obtaining consent: the single and double opt-in.
Single Opt-In
A single opt-in is a data capture mechanism featuring a space for an email address, a consent form, and a submit button. As long as the mechanism meets the guidelines outlined above, then a single opt-in form is compliant with GDPR.
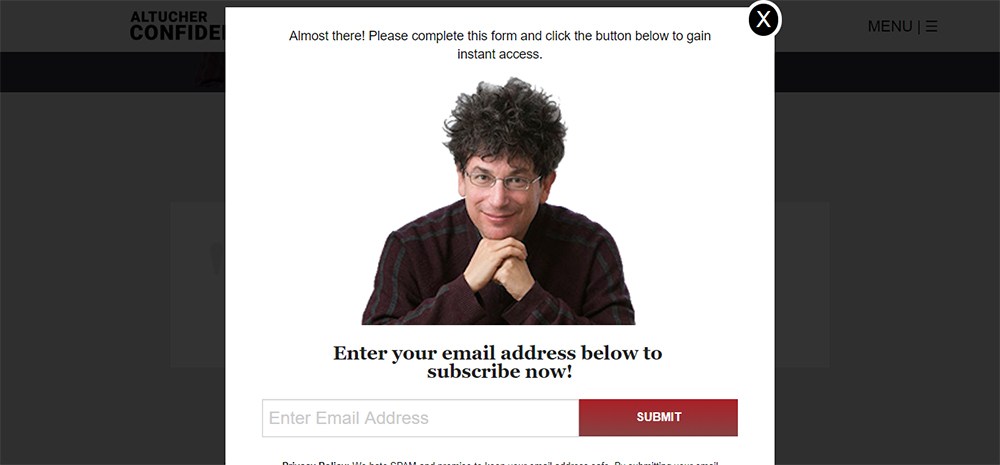
Here's an example of how Altucher Confidential uses a single opt-in form when asking for email addresses.
Here you see two pages: one promises to respect your privacy and not to spam you:
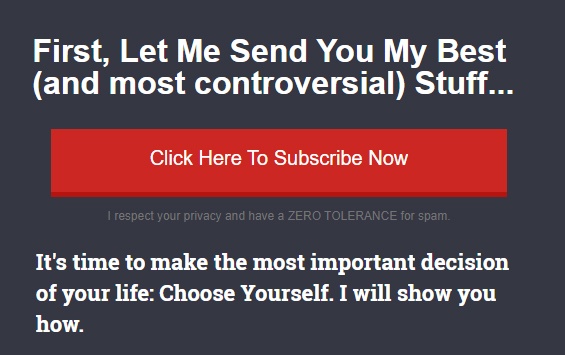
The second asks for your email address. It's simple, honest, and positive. Given the site owner upholds their other data obligations, it meets GDPR standards:
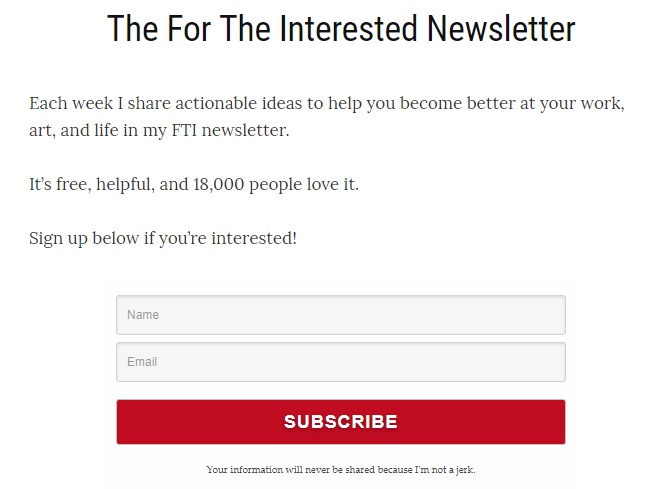
For the Interested also runs a newsletter service with a single opt-in method. Their page is simple: enter your name and email in exchange for a newsletter and promise to never share your data:
Pros of Single Opt-In
- Minimizes barriers to subscription
- Grows larger email lists
- Lower failure rates (15%)
- Can be GDPR compliant
Cons of Single Opt-In
- Complicated forms due to new requirements
- Potential for broken, spam, or fake emails
The Double Opt-In
Some marketers add an extra step for a double opt-in.
The double opt-in includes the same form found in the single opt-in. Then, your email system sends a test email that welcomes your new subscriber and requests a second act of consent: clicking a link.
A double opt-in is also referred to as a confirmed opt-in. You only get a new subscriber when the owner of the address clicks the confirmation link in the confirmation email.
Double opt-ins aren't mandatory, but they're good practice. They make it easier to be GDPR compliant.
Here's an example of a double opt-in email from FreshMail:
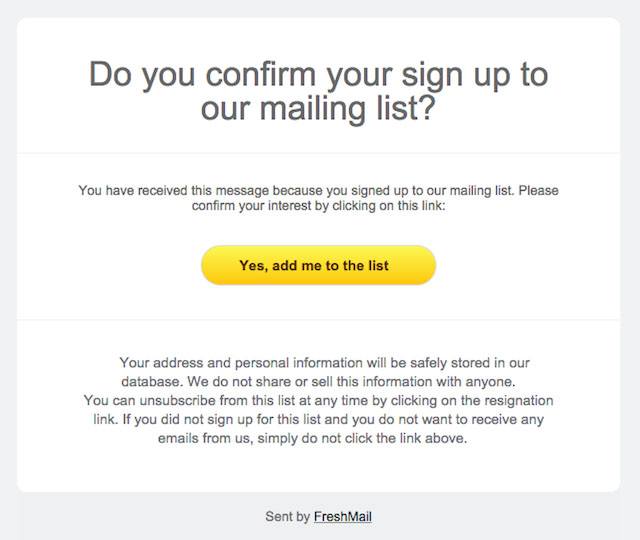
The email requires a second confirmation click and hits all those GDPR requirements. It has informed consent and an easy way to unsubscribe from future emails.
Pros of Double Opt-In
- Easier GDPR optimization
- Encourage quality of list
- Option to improve engagement with initial email
- Better open rates and higher click through rates
Cons of Double Opt-in
- Greater failure rates (27%)
- Less burdensome methods of promoting list quality
Whether you choose a single or double opt-in mechanism is up to you and your audience.
If you cater to an audience who might find email confirmation confusing, do your best with a single opt-in.
Working with a web savvy group committed to getting your emails? Use double opt-in for easier optimization.
Make Unsubscribing Easy

Under the GDPR, complying with consent rules means you need to make it as easy as possible to unsubscribe from your emails.
One option is to add an Unsubscribe link to the footer of all of your emails. Newsletter services like MailChimp offer this as an added option within their templates.
Here's an example of such a link in an email from Frontier Airlines:

Don't forget to make your Unsubscribe feature granular. You'll save more subscribers from leaving completely while also giving customers more of what they want.
The leisure site Jetsetter does a good job of creating granular email preferences:
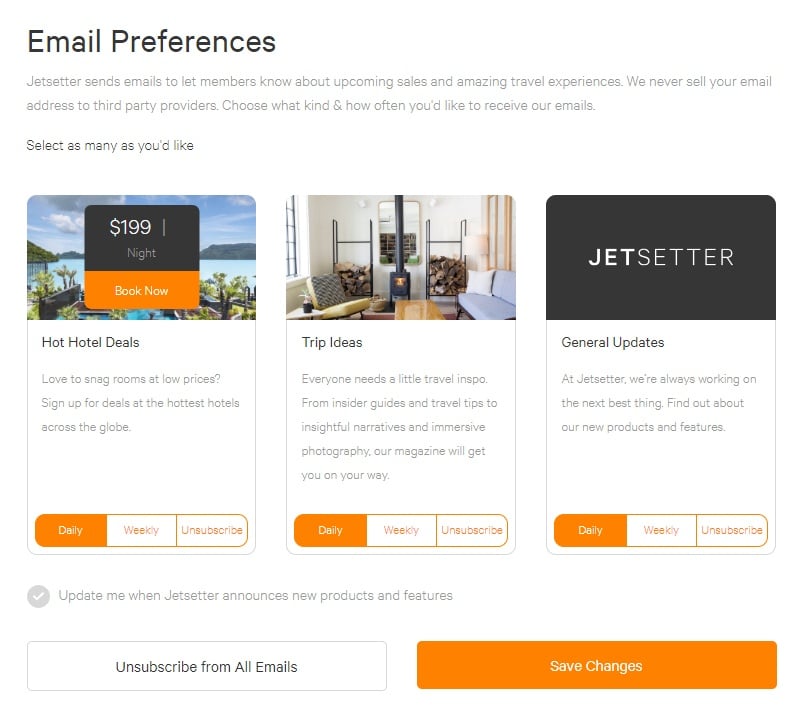
You'll see options to unsubscribe from all the emails or to edit subscriptions to ensure you're only getting the emails you want when you want.
Plus, there's a big 'unsubscribe from all' button at the bottom to make it simple and GDPR-friendly.
Conclusion
If you're collecting personal data (i.e. email addresses) from the EU market, you must comply with the GDPR.
Creating GDPR-friendly newsletters is simple and relies on creating a consensual relationship that allows customers to see exactly what they're signing up for and gives them an opportunity to unsubscribe if they don't like what they see.
Many of these features are already available with email marketing services and form generators.
Just remember that consent for email marketing activities is only one part of the whole GDPR puzzle - what you do with that data matters just as much as how you got it.

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.



