Data breaches have always been a stress point among businesses big and small. In our world's increasing dependence on online services, storage and accessibility, data breaches are becoming a bigger problem than ever before. In 2018 alone, the numbers of people said to be affected by data breaches are in the billions.
- 1. Why Data Breaches Matter
- 2. What is a Data Breach?
- 2.1. Sensitive Data
- 2.2. Data Breach Causes
- 3. Preparing for a Data Breach
- 3.1. Train Employees
- 3.2. Enforce Strong Passwords
- 3.3. Two-Factor Authentication
- 3.4. Monitor Data Transfers
- 3.5. Have a Breach Recovery Plan
- 4. What to Do After a Data Breach Occurs
- 4.1. Confirm the Breach
- 4.2. Isolate the Issue
- 4.3. Fix the Breach
- 4.4. Assess the Damage
- 4.5. Acknowledge Your Legal Responsibility
- 5. Summary
Though dealing with the threat of data breaches can seem like an impossible task, you can protect your business and your clients by better understanding what a data breach is, and by following the tips below.
Why Data Breaches Matter
Imagine waking up one morning, going about your day as usual, when suddenly you receive a call. To your surprise, it's a debt collection agent calling to collect on the thousands of dollars of debt you've recently accrued. The problem is, you never opened that account nor spent all that money.
You try to tell the agent that you are not the one responsible, but good luck convincing them otherwise. The problem takes months to resolve, and in the meantime several other fake accounts are created using your info. By the end of it all, you are proved innocent, but your credit score is in ruins.
This is the kind of situation that can come about from a data breach. It's important to remember the consequences when protecting your clients' and employees' information.
You are responsible for the data you collect as a business. The data you possess can allow people to steal people's identities, steal money, or extort people and ruin reputations. It can also damage your reputation as a business. If you are not trustworthy with your security, no one will want to give your their information or their business anymore. You may also face legal troubles and regulatory fees due to a data breach.
In 2017, the company Equifax suffered a data breach in which they lost around 145.5 million records. To make matters worse, Equifax became known throughout the following year for a series of errors in its handling of the breach. This breach and the subsequent bungling of it eventually cost the CEO of the company his job.
With these examples it becomes easier to see how data breaches can harm both client and company. Because of this it is all the more important to have a solid plan in place to avoid and handle data breaches, and to communicate openly with each other about these events if they do occur.
What is a Data Breach?

A data breach is the extraction or loss of data. It is important to remember that data breaches are not always carried out by malicious hackers. Sometimes a data breach can simply be an accident. It is possible to lose data every day on your own, or to allow private data out into the world due to negligence.
Sensitive Data
Sensitive data is any data that a customer expects to be protected, or any data that could harm you and your business if put into the wrong hands. Below is a list of some of the different kinds of sensitive data that your business is likely to be in possession of:
- Passwords
- PII (Personally Identifiable Information) and other personal data
- Mailing addresses, names, email addresses
- SSN
- Financial Information
- Credit card numbers
- Bank account numbers
- Other personal records
- Money transactions
- Medical records
- Field of business-specific data
- Trade secrets
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is a legal term existing in many state statutes concerning data breaches. Even so, it is a loose term and you may have to check your state's statutes, like the one for New Mexico below, to get a solid definition:

To summarize, this state considers PII to be a name, paired with any one of the other identifying documents or numbers. These two data points can get an identity thief everything they need to take advantage of your and your money.
Data Breach Causes
There are several different types of data breaches, both accidental and targeted. These are a few of the situations that can allow a data breach to occur:
- Weak passwords
- Human error/process failure
- Software vulnerabilities
We'll get into more of each of these later as we talk about how to defend against these situations.
Preparing for a Data Breach

To counter the situations listed above, here are some steps you can take to prevent a data breach.

To help prevent data breaches at your business:
✓ Train employees
✓ Enforce strong passwords
✓ Use two-factor authentication
✓ Monitor data transfers
✓ Monitor data transfers
✓ Have a breach recovery plan
test
Train Employees
- Hire trustworthy people
- Enforce strict data sharing procedures
- Test and audit external communication
- Limit access to sensitive data
Training your employees to correctly handle sensitive data and only share it in the most restricted circumstances is extremely important. Kaspersky Labs reported that "Around nine-in-ten [businesses] that have experienced a data breach [...] said social engineering was part of the attack."
Social engineering in this sense refers to the tactic of trying to extract sensitive data through simple communication with employees and clients in a dishonest way in order to get them to slip and give away the sensitive data. There are a few different types of social engineering attacks, detailed more here, but the most important one to understand, and the one discussed above, is also called phishing.
The only way to beat this is to practice such scenarios and have strict guidelines enforced for how to discuss sensitive data with clients. If you are looking for a way to test and improve your employee security procedures, you can try to utilize the tools of a security consulting group like Infoseq.
Or, you can use an example like the one shown in the picture below. Through a series of questions, one man was able to go from knowing nothing about a large company to convincing an employee to download malicious software. The only way to combat attacks like these are to practice good policy about sharing data through email and over the phone.
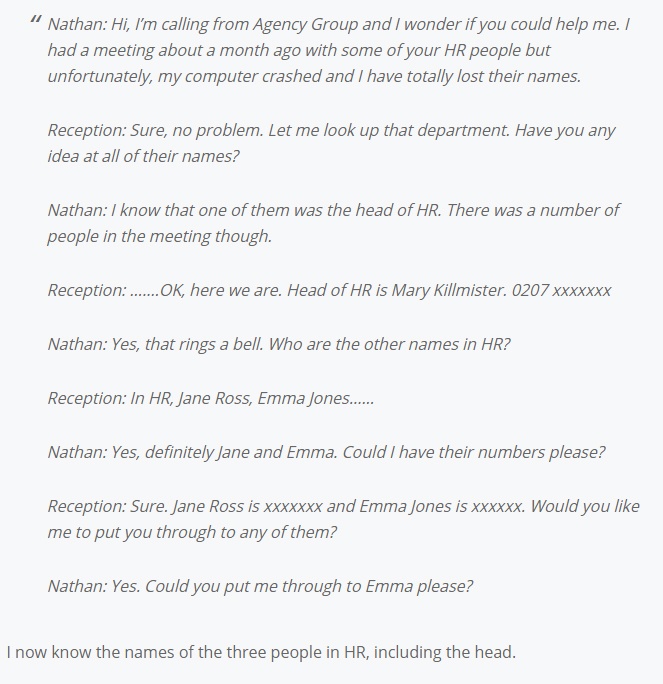
So much of your business security depends on the trust you place in your own employees. If one of your own is a weak link, whether through malicious intent or just complacency, it becomes so much harder to keep your company secure. Start at the beginning by interviewing for data security understanding and ethics to make sure you hire trustworthy people.
Enforce Strong Passwords

These days, many more websites are jumping on the security bandwagon of enforcing strong passwords. These often require a certain length, and at least one of a letter, a number, and a symbol. One downside to this is that passwords are becoming harder than ever to remember, and that is a security threat in and of itself as it leads users to write down their passwords in insecure locations.
A solution for this that many companies are turning to is the use of a password manager tool. This tool keeps all your passwords in one place (kind of like that spreadsheet on your desktop, or the back page of that notebook), but the upside is that it stores all this behind a master password and usually some other form of authentication. On top of this, many of these plug right in to your browser so your passwords are never actually visible on screen, which is a major plus for avoiding any wandering eyes.
Here are two notable password management tools to consider implementing:
LastPass is has a browser extension that makes things extremely simple. Below you can see an example of the vault where passwords, notes, addresses, etc. can be stored privately, all behind a master password.
Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication requires that you have two separate proofs that you are who you say you are to gain access to the site or software in question. One proof is almost always a password, but the second can be many things, including a code texted to your phone or sent to your email address.
Enabling two-factor authentication is a huge leap for your business's security, and highly recommended.
Monitor Data Transfers

Monitoring the transfer of data outside of and within your business is an extremely important way to defend against data breaches. Calls should be monitored and retrievable. Emails should be accessible by a security administrator for all work accounts. This should be possible if you have everyone under a domain, and made even easier if you are using a cloud domain solution like Office 365, which has email tracing for administrators right from the browser.
Have a Breach Recovery Plan
No matter how many precautions you take, there is always the possibility that your business will suffer from a data breach anyways. If and when this happens, you'd better be prepared. Let's talk about that more.
What to Do After a Data Breach Occurs

You'll note that the last step is having a recovery plan. This is important because often one data breach can cause a chain reaction of security breaches that build on each other. Because of this, it's important to have an effective and expedient plan to deal with a data breach once it occurs.
Here's how you can stop a breach from getting worse once it's started.
Confirm the Breach
We have reached this step with the understanding that you have already determined that you've suffered a data breach. Was it reported to you by a victimized client? Did some suspicious traffic show up in your network logs? Are you suddenly and inexplicably missing huge portions of your database?
All of these and more could be the first signs that you are suffering from a data breach. The first step is determining whether or not this is actually a breach and not just a case of misplaced blame or misplaced data.
Isolate the Issue
Most often, the most immediate problem is that a password has been compromised, or a server or database has been accessed through some kind of back door. If this is the case, it's time to bring the server offline immediately if your business can afford to. Your system administrator or a trained security professional should then run diagnostics to determine what exactly was lost and how.
Fix the Breach
Usually a breach is not difficult to fix once it is discovered. Oftentimes it is as simple as changing a password, but in other cases it could mean changing the passwords of your domain, or restructuring your entire network security.
Leave it to a trained and experienced system administrator to determine the extent of the breach and what needs to be fixed.
Assess the Damage
Once you have determined the point of entry and stopped the gap in your defenses, it's time to assess the damage.
When determining what data has been compromised, you'll have to assume the worst. If it seems like a hacker temporarily gained access to a database, you'll have to declare the whole thing compromised even if no one is ever affected. In many cases you may never know the true extent of what has been stolen, which is one reason why data breaches are so expensive.
Acknowledge Your Legal Responsibility
Each state and even countries have their own requirements about what you need to do in case of a data breach. Some of these differences include:
- The definition of sensitive information
- The timing and contents of the Data Breach Notification sent to affected parties
- The conditions for when authorities must be notified
- Punishments in case the statute in question was violated
Below you can see a simple summary of the New Mexico statutes, for example. (See page 44):

If you do international business and have information from users around the world, you'll need to be familiar with some important statutes that deal with protecting data such as the GDPR.
Summary
To summarize, data breaches are extremely costly for both your business and your clients. Whether it is accidental or malicious, loss of any kind will be harmful. Please consider the points listed below when dealing with a possible data breach in your business:
- Train your employees to be aware of and resilient to social engineering and scams
- Enforce strong passwords on all workplace devices and accounts
- Enable two-factor authentication to make your passwords even more secure
- Monitor all data transfer and communication, both with the company and to the outside world
- Have a data breach recovery plan in place
- Confirm the company has actually been attacked
- Isolate the problem and fix the breach
- Assess the damage and acknowledge your legal and ethical responsibilities

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.



